In the realm of real estate risk management, traditional methods have often relied on broad metrics like postcode areas to evaluate exposure and concentration risks. However, this approach often overlooks the nuances and specific risks associated with exact locations. With advancements, a more precise method has emerged, utilising geocoordinates and distance measurements between properties to provide a far more accurate assessment of risk. This article explores the advantages of this modern approach over the conventional postcode-level analysis.
The Limitations of Postcode-Level Analysis
Postcode-level concentration has long been the standard for assessing risks in property-related ventures. Insurance companies, real estate investors, and financial institutions have used this method to gauge potential exposure to various risks, including natural disasters and market fluctuations. However, the granularity of postcodes can vary significantly, with some encompassing vast and diverse geographical areas. This lack of specificity can lead to significant discrepancies in risk assessment, potentially overlooking localised threats such as flooding or urban heat islands.
Advantages of Geocoordinate-Based Assessment
- Precision in Risk Localisation: Geocoordinates offer exact location data, enabling analysts to pinpoint properties and assess risks with much greater precision. This method allows for a detailed understanding of how close a property is to high-risk zones, such as flood plains, wildfire zones, or industrial areas.
- Accurate Measurement of Exposure and Concentration Risks: By calculating the exact distances between properties, it becomes possible to accurately measure risk concentration. For instance, in areas prone to earthquakes or hurricanes, understanding the clustering of properties can help in modelling potential impact scenarios more accurately.
- Improved Risk Mitigation Strategies: With precise data, it's easier to develop targeted risk mitigation strategies. For example, if a group of properties within a specific radius is identified as highly susceptible to flooding, localized flood defenses can be designed and implemented effectively.
- Enhanced Pricing Models: Companies can use detailed location data to create more accurate pricing models. This precision allows for rates that reflect the true risk of specific locations.
- Dynamic Risk Monitoring: Geocoordinates enable real-time risk monitoring. As environmental conditions change, such as rising water levels in nearby rivers, analysts can quickly adjust their risk assessments for properties based on up-to-date proximity data.
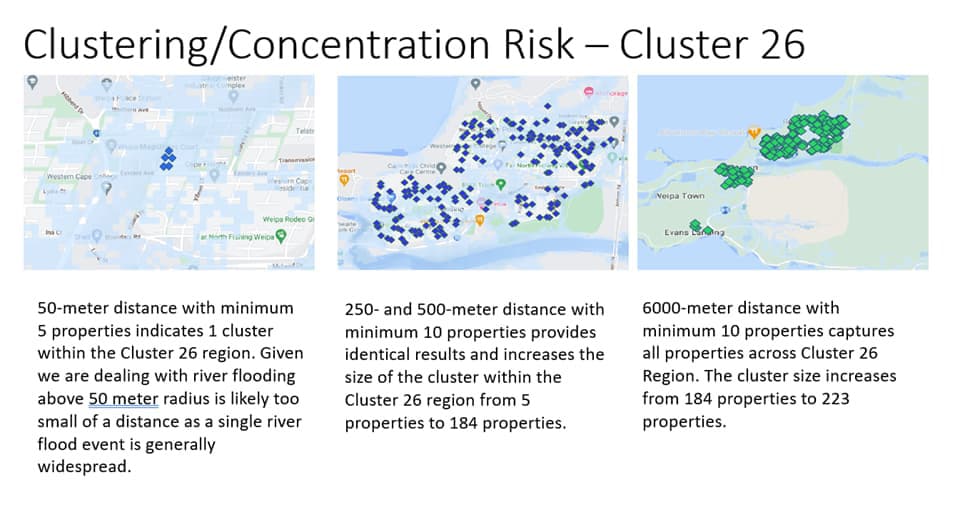
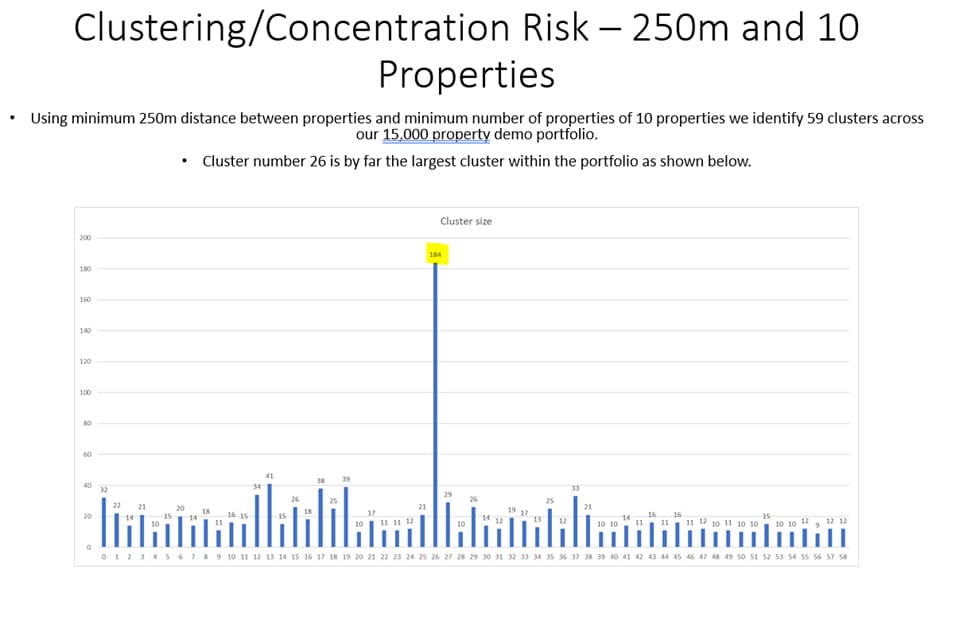
Climate Mapping Services Pty Ltd have successfully implemented geocoordinate-based risk assessment systems in analysis of concentration risk. Through use of our internally developed algorithm we quickly identify pockets of risk concentration across large portfolios using only 2 prescribed variables. Minimum distance in meters between properties and minimum number of properties that form a cluster.
An example below shows how our algorithms identify concentration risks across a large portfolio of loans.
Conclusion
The transition from assessing risks at the postcode level to using geocoordinates and distances between properties represents a significant advancement in property risk management. This method provides a nuanced, precise, and dynamic approach to understanding and mitigating risks, which is particularly crucial in an era of changing climate and evolving urban landscapes. As technology continues to advance, the adoption of geocoordinate-based risk assessment is likely to become a standard practice, offering a competitive edge to those who embrace it early.






