In the rapidly evolving field of climate mapping, geocoding is a critical tool that enables accurate, location-based insights. It serves as the bridge between raw geographical data and actionable intelligence, particularly in areas such as flood mapping. But what exactly is geocoding, and how does it contribute to understanding and mitigating flood risks?
"We specialise in cleaning dirty address data both residential and commercial in order to enable geocoding of each individual property."
What is Geocoding?
Geocoding is the process of converting descriptive location data, such as addresses, place names, or postal codes, into geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude). These coordinates can then be plotted on a map or analyzed in geographic information systems (GIS) for various applications.
For example, if you input an address like "123 Main Street, Anytown," geocoding transforms it into precise coordinates like 40.7128° N, 74.0060° W. This conversion allows locations to be visualized and analyzed spatially, providing a foundation for mapping and geospatial analysis.
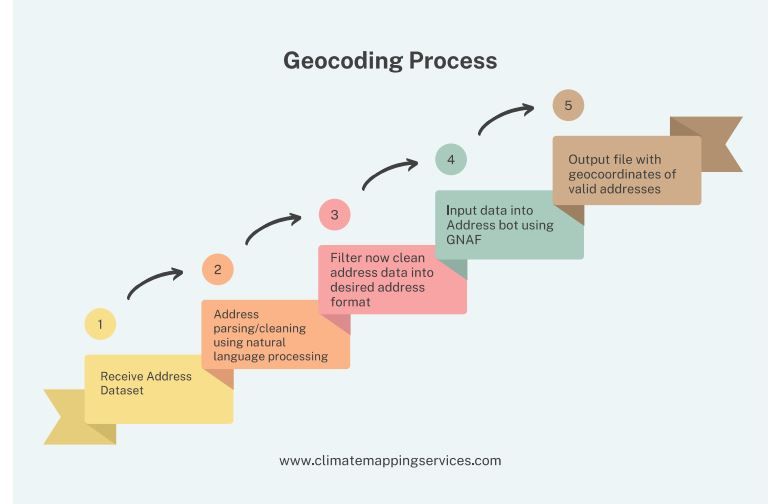
How Does Geocoding Support Flood Mapping?
Flood mapping requires highly accurate, location-based data to predict, visualize, and mitigate flood risks effectively. Here's how geocoding plays a pivotal role in this process:
Mapping Vulnerable Areas
Geocoding helps pinpoint locations at risk of flooding by associating them with geographic features such as rivers, floodplains, and elevation data. When combined with hydrological models, it enables the creation of detailed flood risk maps that highlight areas prone to inundation during heavy rainfall or rising water levels.
Integrating Diverse Datasets
Flood mapping often relies on multiple datasets, such as historical flood records, rainfall patterns, and land-use data. Geocoding allows these diverse datasets to be harmonized by providing a consistent spatial reference. For instance, property addresses can be geocoded and overlaid with flood hazard zones to assess specific risks.
Monitoring and Prediction
When integrated with real-time data, such as weather forecasts and river gauge readings, geocoded locations can feed predictive models. This enables dynamic flood mapping that adjusts to changing conditions, providing communities with timely alerts and actionable insights.
Key Benefits of Geocoding for Flood Mapping
- Precision: Enables highly accurate spatial analysis to identify and address specific flood risks.
- Scalability: Can be applied to local, regional, or global datasets, making it versatile for flood mapping at any scale.
- Interoperability: Works seamlessly with GIS and other mapping tools, ensuring smooth data integration.
- Actionability: Provides the geographic foundation needed for informed decision-making and risk mitigation.
Challenges and Considerations
While geocoding is a powerful tool, its effectiveness depends on data quality. Inaccurate or incomplete address data can lead to errors in mapping and analysis. Moreover, geocoding alone cannot account for complex variables like terrain or hydrology, which require supplementary datasets and advanced modeling techniques.
The Future of Geocoding in Flood Mapping
As climate change intensifies the frequency and severity of floods, geocoding will continue to play an essential role in flood risk management. Innovations like machine learning and AI are enhancing geocoding accuracy and efficiency, while advancements in satellite imagery and sensor technology are enriching the data available for analysis.
At Climate Mapping Services, we specialize in leveraging geocoding and cutting-edge mapping technologies to deliver comprehensive flood risk solutions. Whether you're a city planner, developer, or environmental researcher, our tools empower you to make data-driven decisions and build more resilient communities.
Contact us today to learn how our geocoding-powered flood mapping solutions can help safeguard your community and assets from flood risks.






